Idorsia - SynapCell Collaboration
Home » Resources / Blog / Promising antiseizure effects of Apinocaltamide, developped by Idorsia
Triple T-type calcium channel blocker ACT-709478 (apinocaltamide), Displays Antiseizure Effects in the GAERS Model of Epilepsy Absence
We are thrilled to share the promising results of a recent study on Epilepsy conducted by Idorsia, where SynapCell played a key role in assessing efficacy through preclinical EEG testing. Our collaboration has yielded valuable insights, and we’re proud to have contributed to the advancement of epilepsy research.
This study has just been published in “Antiseizure potential of the triple T-type calcium channel blocker ACT-709478 (apinocaltamide) in rodent models”, Kessler et al. 2025.
As part of a comprehensive set of well-established Epilepsy models, the antiseizure effects of Idorsia’s molecule Apinocaltamide were evaluated in the Genetic Absence Epilepsy Rats from Strasbourg (GAERS*), using in vivo EEG tests in freely moving animals.
Apinocaltamide's effect on absence seizures
The results demonstrated that Apinocaltamide is effective across several epilepsy models, both as a monotherapy and in combination with valproate. Notably, in the GAERS model, Apinocaltamide significantly reduced seizure activity in a dose-dependent manner. Given the GAERS model’s strong predictive validity for absence epilepsy, these findings position Apinocaltamide as a promising therapy for this challenging condition.
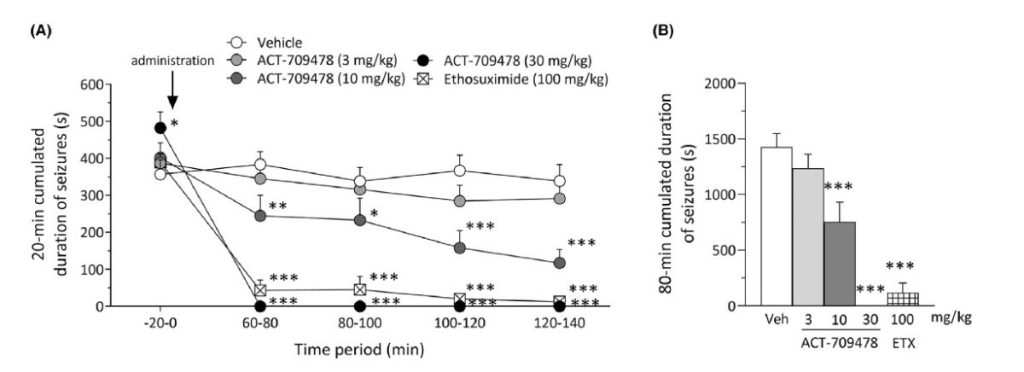
Effect of ACT-709478 on absence-like seizures in Genetic Absence Epilepsy Rats from Strasbourg (GAERS). Cumulated duration of seizures integrated over (A) 20-min periods and (B) entire 80-min periods following single oral administration is shown. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 9–10/group. Mixed-effects model followed by Tukey post hoc analysis: *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001 versus vehicle. ETX, ethosuximide.
