PARKINSON's DISEASE
Home » Solutions / Drug Efficacy Testing / Movement Disorders / Parkinson's Disease
Side-effects and Tachyphylaxis: Room for Improvement of the Standard of Care
The prevalence of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) has doubled in the past 25 years*. This neurodegenerative disorder affects 0.3% of the world’s population and increases with age (1% in people over 60 and 4% in those over 80). It is characterized by degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra and aggregation of alpha synuclein and Lewy bodies, resulting in tremors, akinesia and bradykinesia.
To this date, most of the effective treatment are inducing side-effects, such as the Levo-dopa Induced Dyskinesia (LID), due to the mechanism of action of the compound. However, there is a lack for alternative as challenges such as the intricate molecular mechanisms, coupled with the blood-brain barrier’s selective permeability, that complicate the search for effective drugs. As symptoms become resistant in advanced stages, the industry strives for personalized approaches and reliable biomarkers. The journey from lab to market is long and costly, demanding innovative strategies and collaborative efforts to unlock new therapeutic frontiers.
BetaPark EEG Biomarker and 6-OHDA Rat Model:
SynapCell's Preclinical Alternative to Boost Parkinson's Drug Discovery
SynapCell developed a full spectrum of translational EEG services to address Parkinson’s Disease using validated biomarkers of the disease at different stages. From symptomatic phase to LID, we can offer an A-to-Z evaluation of your compound.
Our in vivo translational and predictive EEG Biomarkers combined with reliable and specific models approach is what makes us unique. Our 6-OHDA freely moving rat model is clinically-relevant, non-behavior based, robust and objective. It is associated with BetaPark, the most translational EEG biomarker of Parkinson’s disease, that is progressively expressed in both PD patients and animal models (6-OHDA rat, MPTP, NHP MPTP…), for predictive and high-quality assessment of your drug candidates. The parallel with the clinic lies in the pharmacology and the EEG-based deficits that are found in both human and the 6-OHDA rat.
The 6-OHDA, a Reference Model for Parkinson's Disease
The model reproduces the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons which translates into EEG deficits as well as Abnormal Involuntary Movements (AIMs) when about 70% of the neurons are degenerated.
It displays the EEG biomarker BetaPark, an abnormal beta oscillation in the motor cortex, similar to that observed in patients and other models of PD.

BetaPark, a Translational & pharmacosensitive EEG Biomarkers of Parkinson's Disease
The reason for the success of this model lies on its EEG biomarker that shows an abnormal oscillation on the EEG spectrum, centered around the Beta frequency (12-30 Hz), called BetaPark.
Sensitive to dopaminergic agonists, this biomarker is therefore also validated by the pharmacology of reference and represents an important and crucial tool in drug development for PD candidate.

One Model for Two Applications
Besides the symptomatic phase and the BetaPark biomarker, this model also shows another perquisite. Indeed, a second use for the 6-OHDA rat is the testing of compounds against LID, such as amantadine. There are two possibilities to de-risk compounds:
Investigate the potential dyskinetic effect of your compound on acute dosing, or after a chronic treatment with L-Dopa.
Key Features
of the 6-OHDA Model
The 6-OHDA model is considered a gold standard for drug discovery in Parkinson’s disease:
- Selectively targets dopaminergic neurons, mimicking the disease’s pathology
- Reproduces motor deficits similar to Parkinson’s symptoms
- Enables study of disease symptoms
- Produces reproducible lesions
- Permits long-term evaluation of drug effects
- Compatible with various assessment techniques
It is a reliable platform for evaluating potential Parkinson’s treatments in preclinical research.
6-OHDA rat model shows the same disorders as in human Parkinson’s disease over time, making it the ideal model to test drug efficacy for PD.
The first lesion is quite fast (4-5 weeks) to generate the first biomarker (BetaPark) but the model is then stable for several weeks, even months. This allows for longitudinal studies, either long chronic treatment or crossovers with several conditions (up to 10).
SynapCell’s 6-OHDA rat model shows a translational and relevant pharmacology. Indeed, in this model, the dopaminergic agonists such as ropinirole, L-DOPA, apomorphine and SKF-38393 display a dose-dependent effect on BetaPark reduction.
Along the same lines, the LID biomarker, GammaPark, also shows a pharmacosensitivity to amantadine, the standard of care on the market.
Drug Discovery Assays with the 6-OHDA Model
Similarly to many of the models in our portfolio, this model is stable over time and therefore offers the possibility to perform crossover designs.
These types of designs are well-suited for drug discovery as they reinforce the statistical power of the data generated, limit the number of animals used and allow a relatively fast turnaround for the first results.
In these settings, you’re able to select the most promising candidate amongst a library of compounds, and/or perform another crossover to fine-tune the efficacious doses of your lead asset.
Assess how a compound’s effects change with varying doses, and analyze the relationship between dose and response, examining efficacy, safety, and biological effects across different concentrations to determine optimal dosing strategies.
Subtle effect can be highlighted thanks to the precision of EEG and the BetaPark biomarker, allowing the dose-response curve to be as accurate as possible.
Simulate the effects of short- and long-term levodopa (L-DOPA) treatment in Parkinson’s disease to study drug efficacy, side effects and disease progression on different time scales.
The acute effect of L-DOPA allows for a very good positive control for the treatment of the symptoms while also offering a good control for the undesirable side effects (Gamma peak).
POSTER
Improving Drug Discovery in Parkinson's Disease Using Brain Oscillations as Translational Biomarkers
In this Poster, we investigate the use of aberrant cortical oscillations as translational biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease Drug development and evaluate the effect of acute (L-Dopa, Apomorphine) and chronic (L-Dopa) treatments on both EEG oscillations and Abnormal Involuntary Movements (AIMs) in the 6-OHDA model.
DOWNLOAD
POSTER

Powered by Cue®, SynapCell's Predictive In Vivo EEG Platform
SynapCell’s 6-OHDA rat model and its associated EEG biomarker (BetaPark) are processed on Cue®, our innovative translational in vivo EEG platform, which is designed to predict the in-human efficacy of your drug candidates during the preclinical step. Cue® is the result of decades of R&D, combining SynapCell’s know-how, expertise and scientific excellence in the fields of brain surgery and EEG signal recording, processing, and analysis.
Using Cue®, we transform preclinical data into actionable insights, offering end-to-end support for informed decision-making in CNS drug discovery.
THE SCIENCE CORNER
BetaPark, a Translational EEG Biomarker
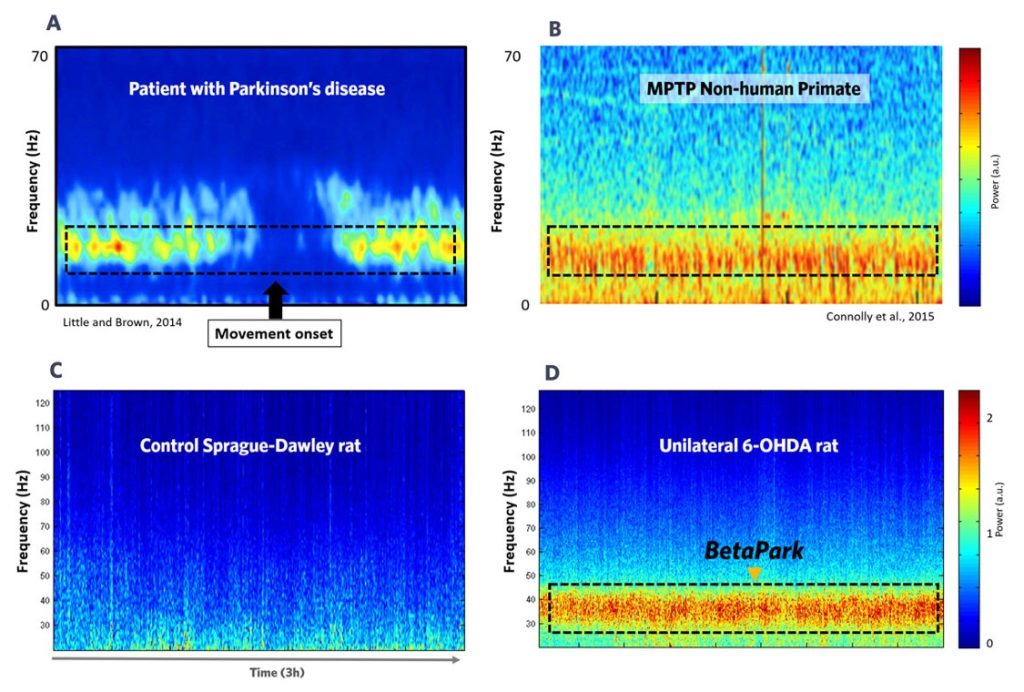
(A) In Parkinson’s Disease patients, an aberrant oscillation, around the beta band, is observed in the cortico-basal ganglia loop.
This aberrant oscillation is modulated by the initiation of voluntary movements, deep-brain stimulation and Dopaminergic drugs.
Adapted from Little and Brown 2014, Curr Biol. 2024 Sep 22; 24(18)
(B) A similar activity is observed in a non human primate model of PD, the MPTP model. In those animals an prominent and aberrant oscillation is as well observed in the cortical-basal ganglia loop.
Adapted from Connolly et al. J neural Eng. 2015 Dec; 12(6):066012
(C) (D) Using the unilateral 6-OHDA lesioned rat model of PD, we found a prominent beta band (betaPark, centered at 30Hz) in the motor cortex (D), which was absent in control Spraqgue-Dawley rats (C).
The translational aspect of the EEG biomarker is greatly reinforced and supported by its presence from human down to NHP and rodent models. The frequencies at which the abnormal oscillations is centered may vary slightly across species, but they are all correlated to movement and sensitive to the same pharmacology, as the next point shows.
Pharmacology of Reference
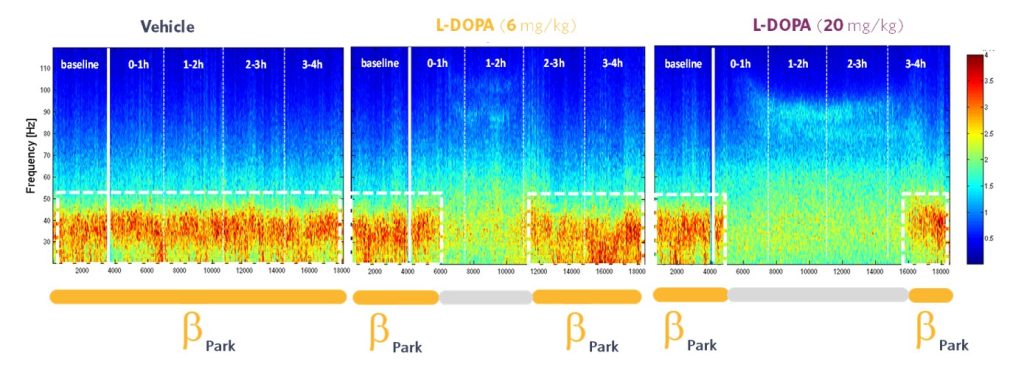
Diving into the details of the BetaPark EEG biomarker, the time-frequency maps above represent the power of the classical frequency bands (1-140 Hz) as a function of time. Abnormal increased power can be seen centered around 30 Hz, and this increase is stable overtime, without pharmacological action.
After administration of L-DOPA, there is a decrease in power observed at this same frequency, lasting for about an hour. This effect is dose dependent, not only on regarding the amplitude of the effect (the higher the dose, the greater the reduction in beta power) but also regarding the duration of the effect. Indeed, as showed on the time-frequency maps, increasing the dose of L-DOPA will induce a longer duration of its effect.
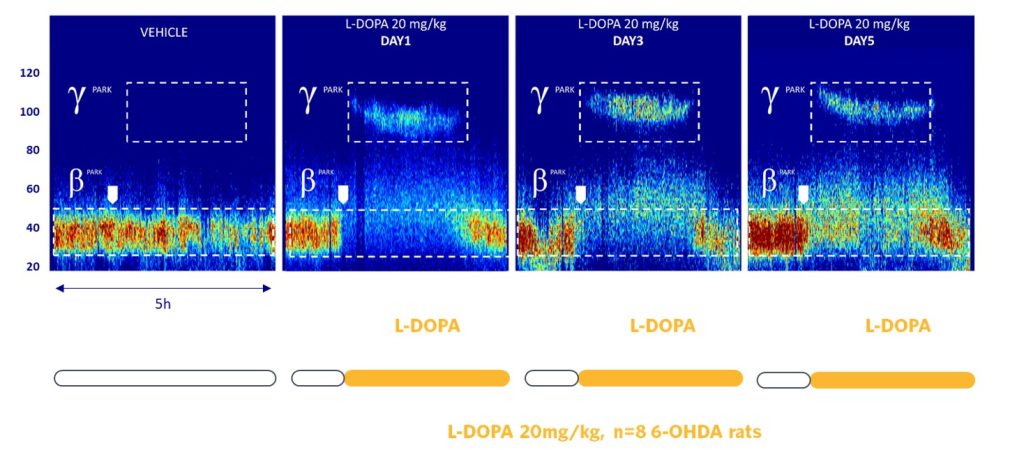
GammaPark, a Dyskinesia-related EEG Biomarker
As hinted before, injection with dopaminergic agonists, can lead to the progressive apparition of dyskinesia and the associated EEG biomarker, GammaPark (90Hz). This phenomenon is appearing at the 20 mg/kg dose, even with an acute condition, and is exacerbated by a chronic treatment. This aspect of the model is also sensitive to standard of care such as amantadine and can be explored, not only to document the effect of a compound against LID, but also to de-risk any compound directed towards symptomatic symptoms of the disease.
For all of that, and more, contact us !
Let's Talk About Your Research Project!
More than a CRO, a team of collaborators – we are your dream neuroscience team specialized in preclinical EEG! We don’t just produce data, we are your partners from conceptualization to conclusion. We translate raw EEG data into meaningful, clinically-relevant endpoints, delivering clear insights to allow data-based decision-making. Choose SynapCell, a leading preclinical CNS-specialized CRO for cutting-edge EEG expertise combined with an irresistible touch of fun.
News & Events
PRESS RELEASE
SynapCell and the University of Utah Celebrate the 10-year Anniversary of their Collaboration on Anti-Seizure Medications.
AES ANNUAL MEETING 2024
Join us at the AES Annual Meeting 2024,
Booth #2141,
Los Angeles, December 6-10, 2024
NEW!!!
Discover SynapCell’s brand new preclinical EEG solutions for sleep architecture and vigilance states.